-
Linked List
A linked list is a sequence of data structures, which are connected together via links. Linked List is a sequence of links which contains items. Each link contains a connection to another link. Linked list is the second most-used data structure after array.
The following code is designed as follows :
1. Class "Node" to declare pointers.
2. Class "Linked List" to design methods which will help user to perform desired operation over their Linked List data structure.
3. Sample Driver Code to demonstrate the functioning of the template.
- Size : Since data can only be stored in contiguous blocks of memory in an array, its size cannot be altered at runtime due to the risk of overwriting other data. However, in a linked list, each node points to the next one such that data can exist at scattered (non-contiguous) addresses; this allows for a dynamic size that can change at runtime.
- Memory allocation: For arrays at compile time and at runtime for linked lists. but, a dynamically allocated array also allocates memory at runtime.
- Memory efficiency : For the same number of elements, linked lists use more memory as a reference to the next node is also stored along with the data. However, size flexibility in linked lists may make them use less memory overall; this is useful when there is uncertainty about size or there are large variations in the size of data elements; Memory equivalent to the upper limit on the size has to be allocated (even if not all of it is being used) while using arrays, whereas linked lists can increase their sizes step-by-step proportionately to the amount of data.
- Execution Time : Any element in an array can be directly accessed with its index. However, in the case of a linked list, all the previous elements must be traversed to reach any element. Also, better cache locality in arrays (due to contiguous memory allocation) can significantly improve performance. As a result, some operations (such as modifying a certain element) are faster in arrays, while others (such as inserting/deleting an element in the data) are faster in linked lists.
- Insertion : In an array, insertion operation takes more time but in a linked list these operations are fast. For example, if we want to insert an element in the array at the end position in the array and the array is full then we copy the array into another array and then we can add an element whereas if the linked list is full then we find the last node and make it next to the new node Dependency: In an array, values are independent of each other but In the case of linked list nodes are dependent on each other. one node is dependent on its previous node. If the previous node is lost then we can’t find its next subsequent nodes.
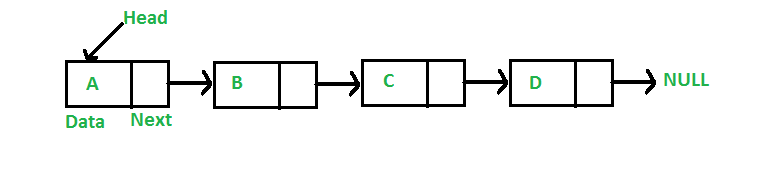
A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at
contiguous
memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers as shown in
the below
image:
Major differences between array and linked-list are listed below:

Major differences between array and linked-list are listed below: